Python - Perfect Number or not
Problem Statement
Brief Description
According to the problem statement we have to write a program in Python that will take an integer value as input from the user through the keyboard and will check whether it is a perfect number or not.
A positive number is perfect if it is equal to the number obtained by adding its proper positive divisors excluding the number itself.
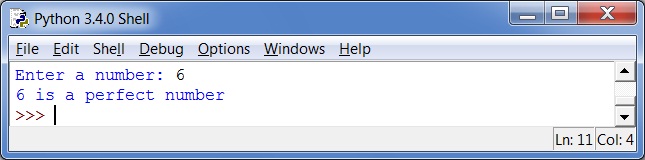
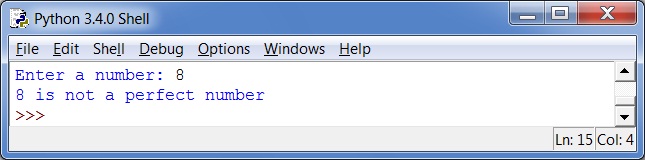
For example, if the user enters 6 as input, the program will generate an output indicating that 6 is a perfect number since the number 6 is divisible by 1, 2 and 3 (excluding 6) and 1+2+3=6. But if the user enters 8 as input, the program will generate an output indicating that 8 is not a perfect number since the number 8 is divisible by 1, 2 and 4 (excluding 8) and 1+2+4=7.
Program
num=int(input("Enter a number: "))
tot=0
for i in range(1,num//2+1):
if num%i==0:
tot=tot+i #OR tot+=i
if num==tot:
print(num,"is a perfect number")
else:
print(num,"is not a perfect number")
Output 1
Output 2
Explanation
- 3 variables namely num, tot and i are used.
- The integer value entered by the user is stored in num.
- Initially 0 is stored in tot.
| num | num%i==0 | tot=tot+i; | tot | i | Comment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6 | ----- | ----- | 0 | 1 | Initial Values |
| 6 | 6%1==0 ↓ 0==0 ↓ True | tot=0+1; | 1 | 2 | Iteration 1 |
| 6 | 6%2==0 ↓ 0==0 ↓ True | tot=1+2; | 3 | 3 | Iteration 2 |
| 6 | 6%3==0 ↓ 0==0 ↓ True | tot=3+3; | 6 | 4 | Iteration 3 |
- At first 1 is stored in i.
- The value of i is checked with respect to the stop value i.e. num//2+1.
- If value of i is less than num//2+1, the statement written within for loop is executed and the loop continues to iterate till value of i is less than num//2+1.
- If value of i becomes equal to num//2+1 then the loop stops working and the control goes to the statement written immediately after the loop.
- At the end of each iteration the value of i is incremented by 1.
- Within for loop it is checked to see whether the value stored in i is a proper positive divisor of the value stored in num or not.
- If it is then the value stored in i is added with the value stored in tot and the result is stored in the same variable i.e. tot.
- If it is not then the statement written within if statement is not executed.
Thus the above process is used to add the proper positive divisors of the value stored in num excluding the number itself.
The final result is stored in tot.
Finally it is checked to see whether the value stored in num is equal to the value stored in tot. If it is then we can conclude that the value stored in num is a perfect number otherwise not and an appropriate message is displayed on the output screen.
